Dental implants have been a game-changer for tooth loss in today’s dentistry world. But not all implants work. Bad dental implants come with an array of problems, including pain, infection, bone loss, and, in rare cases, implant failure. Knowing the reasons, risks, and remedies can empower patients to make informed choices.
Concerned about Bad dental implants? Discover the signs, causes, and treatment for an unsuccessful implant. Learn professional tips on how to avoid dental implant failure and guarantee longevity!”
🦷 Bad Dental Implants Self-Check Tool
Use this quick checklist to see if you may be experiencing issues with a dental implant.
📘 Educational Info
Dental implants can fail due to infection, poor integration, or poor hygiene. Catching issues early helps avoid serious complications.
Consult a licensed dentist if you suspect any issues with your implant.
What Are Bad Dental Implants?

A Bad dental implant is one that fails, is improperly placed, or fails to integrate, causing you pain, headaches, or infection, which may lead to the removal of the implant or implants. Mechanical failures, infections, or inadequate follow-up care can lead to complications with a success rate of approximately 95% of implants.
Signs of Bad Dental Implants
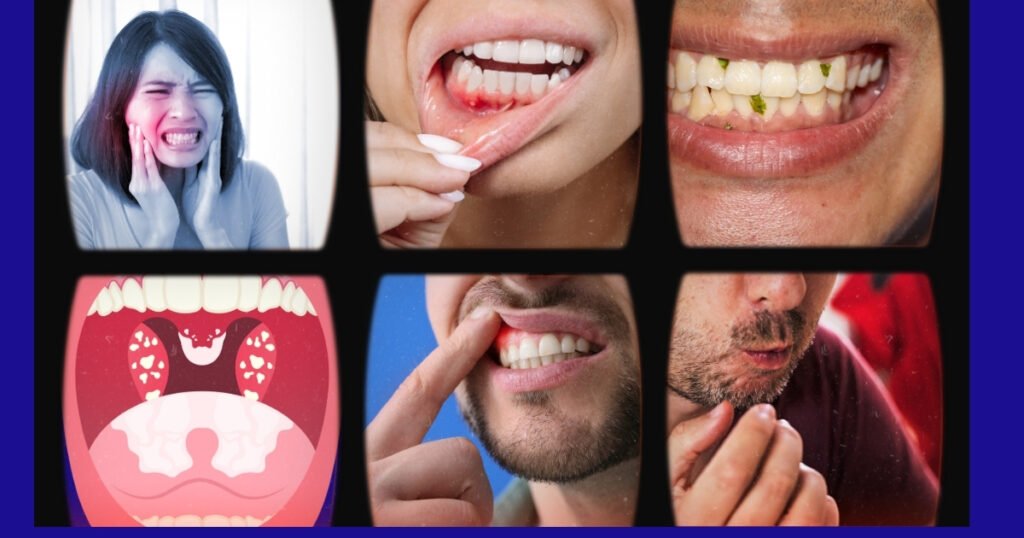
Identifying the early warning signs of implant failure can prevent devastating consequences. Common signs include:
- Chronic pain that lasts beyond the usual recovery time
- Redness or inflammation in the area of the implant
- Loose or shifting implant
- Pus or bad taste that suggests an infection
- Implant Post Exposed Through Receding Gums
- It may be uncomfortable to chew, speak, or yawn.
If any of these symptoms occur, immediate dental consultation is necessary.
When one of these symptoms is present, dental consultation should be sought immediately.
Common Causes of Bad Dental Implants
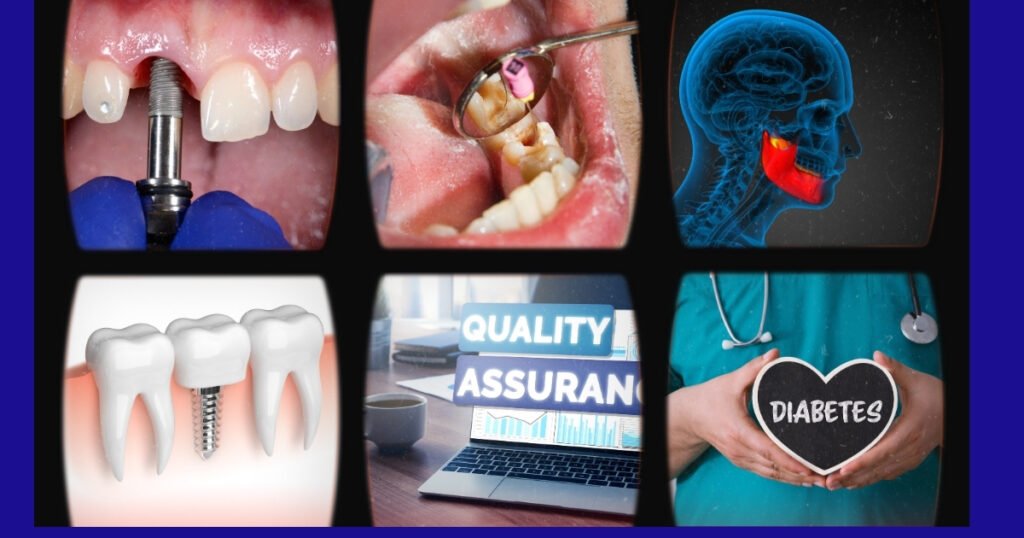
1. Poor Implant Placement
If the implant is not placed properly, then it can lead to biting problems, extrusion of adjacent teeth, and bone loss. It is up to you to have straight teeth in the first place to avoid them becoming crooked in the future
2. Infectious and Peri-Implant Diseases
Peri-implantitis is an inflammatory disease that attacks the gum and bone surrounding the implant, and can result in infection, bone loss, and implant loss. The condition is frequently the result of bad oral care, smoking, or existing gum disease.
3. Insufficient Bone Density
Implants must be well integrated with the host bone. If an individual has lost bone in the jaw due to periodontal disease or an extraction, the implant likely won’t properly integrate, and the procedure would fail. Bone graft is frequently needed in such situations.
4. Poor-Quality Materials
Not all implants are the same. Some materials are cheaper or inferior, and your body may not assimilate them well, leading to rejection or breakage. The majority of research is on titanium and zirconia implants, which are considered to be the most durable and biocompatible.
5. Implant Under Too Much Pressure
If bear more than the instructed pressure on the dental implant (especially during its healing process), loosening or even fracturing may occur. It is a typical symptom of bruxism (teeth grinding) and/or patients who are noncompliant with post-operative care.
6. Pre-Existing Medical Conditions
Some diseases, like diabetes, osteoporosis, or an autoimmune disease, can inhibit the healing process and increase the chance of dental implant failure. Patients who have these conditions should speak with their dentist before making the leap.
Risks Associated with Bad Dental Implants

That can be a problem, as bad implants can cause a range of issues, such as:
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Chronic Pain | Nerve damage or infection can cause Persistent Pain around The Implant. |
| Gum Recession | The gum tissue pulls back, exposing the implant post, leading to discomfort and aesthetic issues. |
| Bone Loss | A sign of an underlying infection that needs immediate treatment. |
| Loose or Shifting Implant | Poor osseointegration (bone fusion) may cause the implant to loosen over time. |
| Facial Swelling & Inflammation | A sign of underlying infection that needs immediate treatment. |
How to correct bad dental implants

Multiple corrective options are available if an implant fails:
1. Implant Removal and Replacement
In severely infected or rejected cases, the implant ought to be removed. After adequate healing — and perhaps a bone graft — a new implant can be inserted.
2. Bone Grafting for Stability
After bone loss has been identified, a graft can be placed to replace the lost bone, and a new implant can be successfully placed.
3. Antibiotics and Infection Treatment
If diagnosed early, deep cleanings, antibiotics, and laser therapy can salvage the implant.
4. Bite Adjustment
For bite misalignment, the dentist would then adjust the crown, abutment or opposing teeth to achieve proper occlusion.
5. Gum Grafting for Receding Gums
A gum graft may be used to replace the lost gum tissue surrounding an exposed implant post, enhancing appearance and stability.
How to Avoid Bad Dental Implants

1. Choose an Experienced Implant Dentist
Always choose to see a well-trained and experienced general dentist or oral surgeon who has dental implant experience/training!
2. Establish an Accurate Diagnosis and Plan
A comprehensive CT scan and digital imaging allow us to evaluate bone density, nerve position, and where the implants should be placed prior to the surgery.
3. Follow Aftercare Instructions for Surgery
Patients must:
- Maintain Good oral hygiene (brushing, flossing, etc.)
- Do not smoke or consume alcohol until the wound is healed
- Maintain a soft diet for the first couple of weeks
- Keep up with dentist appointments
4. Opt for Superior Implant Materials
Choose FDA-certified titanium or zirconia implants over other materials for strength and improved osseointegration.
5. Address Underlying Health Conditions
Patients with diabetes, osteoporosis, and other related diseases need to be treated well before the surgery.
When to Visit the Dentist for Implant Problems

Go to the dentist right away if you have:
- If the pain is intolerable for longer than a few days.
- Loose crown and/or shifting of the implant
- Pus, blood, or bad taste around the area of your implant
- Redness (and perhaps swelling or fever), a sign of infection
Early management spares the implant or provides better options for corrective measures.
Final Thoughts
Although dental implants are a great option for tooth loss, poorly made dental implants can result in painful side effects and expensive fixes. Selecting an experienced dentist, having the right post-treatment care, and treating any existing health issues can all help lower the risk of implant failure. If you suspect that something doesn’t feel right with your dental implant, seek help right away to save it from additional harm and preserve it long after it has been placed.
Also Read-Ultimate Guide to Dental Implants: Everything You Need to Know
Also Read-Zirconia Dental Implants Cost: Pricing, Benefits & What to Expect in 2025!
Also Read-How to Get Dental Implants Covered by Medical Insurance: Insider Tips & Tricks!
FAQs on Bad Dental Implants
How bad do dental implants hurt?
The pain from a dental implant is typically mild to moderate, and it should last no more than a few days following the procedure. Discomfort post-operatively is usually caused by swelling, bruising, or tenderness and is typically well controlled by pain medication provided by your surgeon or over-the-counter analgesics.
What to Know About Dental Implant Pain:
During the surgery, it’s performed under local anesthesia, so there is no pain. In some situations, sedation is needed for additional comfort.
Post Operatively (Days 3 – 5): Pain – mild to moderate, swelling, tenderness normal. Maximum pain is reached within 48 hours and gradually reduces.
One week: The majority of swelling and pain will subside, and most normal activities can be resumed.
Long-lasting Pain (Rare): Pain after two weeks can be a sign of infection, nerve damage, or implant rejection and should be evaluated by a dentist.
Pain Control: Medications to ease pain, as well as the use of ice packs and soft foods, can alleviate discomfort.
The pain of dental implants seems to be less than that of a tooth extraction and is consistent amongst most of the patients.
Is the dentist responsible for a failed implant?

There could be negligence on the part of your dentist if the implant fails because of surgical errors, inadequate pre-op planning, or wrong placement of your implant. But if failures occur due to patient-related factors such as smoking, lack of oral hygiene, or medical conditions, then that is not the dentist’s responsibility.
Under What Circumstances is the Dentist Liable?
Malposition: A case where the implant is in the wrong position, causing it not to work.
Insufficient Bone Review: When the doctor fails to adequately assess for bone density before the implant.
Sterilization Matters: Bad hygiene while operating can lead to infection.
Implant Choice: The implant selected may not be appropriate for the patient’s needs.
Inadequate Post-Operative Care Instructions: Neglecting to give appropriate post-operative care advice.
When is it the Patient’s Responsibility?
Bad Oral Hygiene Leads to higher rates of infection.
Smoking decreases both blood flow and healing.
Medical Conditions: Diabetes, osteoporosis, or gum disease can interfere with healing.
If a dentist’s error led to failure, some form of legal action or a refund could be possible.
What are the symptoms of bad implants?

The worst implant is one that can be identified by symptoms such as unrelenting pain, swelling, or a compromised gum, or a loosening implant. Other signs, such as an inability to chew or pus production , and bad breath, were suggestive of infection or failure of the implant.
Typical Signs of a Bad Dental Implant:
Chronic Pain: Pain that continues past the period for normal healing.
Lumps or Swellings: Possible infection or inflammation.
Implant loosen: A strong implant should not be loose.
Recession of gum: there may not be enough gum to cover the implant, so that it is visible.
Discharge or Bad Taste: Suggests that there is an infection around the implant.
Chewing Discomfort: Pain while chewing or eating could be an indicator that the implant has failed.
These are some of the symptoms you may experience, and you should see your Dentist. Early intervention can help prevent complications and save the implant.
Do you get your money back if a dental implant fails?

Refund policies for unsuccessful implants are at the discretion of the clinic and the reason for failure. The success rates of these devices are hard to estimate, since none of them offer a success refund if the cause of failure is due to a patient’s personal anatomy or caused by a surgeon on behalf of the patient.
Factors Affecting Refunds:
Dentist’s Mistake: If failure occurred due to bad placement or technique, you might be eligible for a refund or a free replacement.
Manufacturer’s Defect: Certain implants are covered with warranties for failure.
Patient Negligence: Whether you are a smoker, lack good hygiene, or suffer from several different medical conditions, you may be ineligible for a refund.
Clinic Policy: Some clinics have free corrections others may charge more.
Insurance: Replacement for some plans may be covered.
Before you have treatment, talk to your dentist about a refund policy so that you know your financial options.
What is the biggest reason implants fail?

Lack of osseointegration is the most common cause of dental implant failure, in which the implant fails to fuse with the bone. This can be caused by low bone density, infection, or overload of the implant.
Main Causes of Implant Failure:
Osseointegration Does Not Occur: The bone fails to unite with the implant.
Infection (Peri-Implantitis) – Bacteria invade the site of the implant and cause an inflammation.
Smoking: Cuts blood flow, slowing the healing.
Weak Bone: If you have a weak jawbone, it may not be able to support the implant.
Bruxism (Grinding Teeth): Apply too much pressure to the implant.
Pathology: Healing may be affected if you have diabetes and osteoporosis.
The risk of failure is also decreased by regular visits to the dentist.
How do you know if your dental implant is infected?
An infected implant can result in swelling, pain, halitosis, pus, and receding gums. It might also seem floppy, or you might have problems chewing. Prompt dental attention is required to avoid the loss of implants.
Signs of an Infected Implant:
Red, Puffy Gums: Irritation With Swollen Tissue Around the Implant.
Chronic Pain: Pain that is persistent beyond the expected time frame of recovery.
Pus or Foul Smelling Breath: Sign of Bacterial Infection 1 There are 4 comments.
Receded Gums: The implant may appear to be more exposed.
Implant Becomes Loose: A well-implanted device should never move.
If these symptoms appear, see the dentist right away for treatment.
Does a failed dental implant need to be removed?

Yes, an unsuccessful dental implant often has to come out to avoid further harm and infection. The dentist may replace it when the bone is healed, but it’s dependent on the state of the bone.
When Removal is Necessary:
Extreme Infection (Peri-Implantitis): Eats away at the bone surrounding the implant.
Implant Loose Implant: It is not working the way it is supposed to.
Failed text: (chronic pain or discomfort); means he failed.
Rejection of the Implant: It isn’t accepted by the human body.
What’s not good: Improper Positioning: It can lead to bite-related issues if it is not placed correctly.
When it is taken out , the site can heal before it is replaced.
How do you know when your implants need replacing?
It may be necessary to replace loose or painful dental implants that show evidence of infection. Implants last for decades in theory, but upkeep, injury, or loss of bone may limit their lifespan.
Warning Signs That Your Implant Needs Replacing:
Loosening: A successful implant should be well fixed in position.
Pain: Constant pain can be an indication.
Receding Gums: The implant may start to show more.
Infection: Look for swelling, pus, or bad breath.
Trouble Eating: The implant might be failing if you are experiencing discomfort during mealtimes.
Regular checkups can aid in early problem detection and the extended life of the implant.
How many times can a dental implant be replaced?

A dental implant can be reimplanted numerous times, but it depends on bone quality. It may be necessary to perform bone grafting if the jawbone is too weak to support a new implant.
Causes for Reimplantation:
Bone Mass: Females need strong bone to hold the implants.
Past Failure Cause: Fixing the cause increases the odds of success.
History of Infections: Multiple infections may have an impact on viability.
General Health: Diseases, such as diabetes, can affect healing.
Quality of Dentist: Disc is retained if placed properly.
Most people don’t require multiple replacements in their lifetime, provided they take good care of them.
Can a dental implant get infected years later?

Yes, a dental implant may become infected even after several years if the hygiene levels are not maintained, if gum disease is present, or if too much stress is put on the implant. If left untreated, this condition, known as peri-implantitis, could lead to bone loss and implant failure.
Source of Infection in Late-Placed Implants:
Lack of Oral Care – Build-up of plaque can cause gum disease.
Peri-implantitis – A gum-disease-like condition that infects implants.
Possibility OF CIGARETTE SMOKING – Increases the chances of infection and impairs healing.
Diabetes or Other Medical Conditions – Suppresses the immune system, which increases the risk of infection.
Too much bite force — The implant can be weakened by grinding or clenching your teeth.
Misplaced Implant – If the implant is placed too close or too far from the bone, it can stress the alveolar bone surrounding it.
How common are problems with dental implants?

Complications with dental implants are very uncommon, affecting 5-10% of patients. Complications can include infection, loss of the implant, and nerve impingement, but with good care and a decent dentist, most are successful – the success rate for implants is up to about 90-95 per cent.”
Common Dental Implant Issues:
Infection (Peri-implantitis) – When bacteria accumulate.
Loosening of Implant – As a result of bone resorption or lack of osseointegration.
Receding Gums – Gums recede, and the implant becomes exposed.
Nerve Damage – Sometimes the implant is inserted too close to the nerve.
Sinus Issues – Upper-jaw implants could infringe on the sinuses.
Bone Resorption – May happen if the implant doesn’t heal properly.
Why do gums recede around implants?
Gums around implants can recede as a result of an infection, bad oral hygiene, or the pressure on the implant may be too great. This leaves the metal post exposed, which can impact appearance and make it less stable.
Causes of Gum Recession Around Implants:
Peri-implantitis – An Infection where gums and bone deteriorate.
Thin Gums – Others simply have thin gums that recede more quickly.
Bad Oral Hygiene – Plaque and bacteria may lead to inflammation.
Too much force – this will put strain on the implant (Biting, grinding)
Poor Placement – If placed too near the gumline, then this can lead to recession.
What don’t they tell you about implants?

Dental implants can fix a missing tooth, but drilling out the implant is a bone-chilling affair that even albeit temporary, induces a lot of overly-negative emotions (not to mention the money). They’re not always a silver bullet, and complications such as infection, nerve damage or bone loss can arise.
What People May Not Understand About Implants:
Not Everyone Will Be a Candidate- Must have enough bone density and healthy gums.
The Process of Healing – Because the bone will need to grow around the implant, it will require several months of healing time.
Complications – Infection, screw loosening, or the gums pulling back.
They Don’t Require Cleanings – Because fake teeth are fake, you never have to clean them!
Can Be Expensive – Implants are quite costly, and insurance plans do not always cover this expensive procedure.
What is the downside to dental implants?

The primary disadvantages of dental implants are cost, healing time, and potential for complications. They are a permanent solution but entail surgery and maintenance.
Drawbacks of Dental Implants:
Expensive – Implants are costly, particularly when several implants are required.
Surgical Risks: Infection, nerve damage, and/or nasal problems may develop as a result of the surgery.
Lengthy Healing Process – The implant, when inserted, needs somewhere between two and six months to integrate with the bone.
Risk of bone loss – Can lose bone if it is not properly maintained.
Not For Everyone – Those with diabetes, who smoke, or have low bone density might not be able to get the treatment.
Who is responsible for dental implant failure?

Blame for the failure of tooth implants depends on what caused the failure. If poor oral hygiene or medical conditions were its cause, the patient is to blame. The dentist could be to blame if the problem was due to careless placement, malpractice, or substandard materials.
Main Reasons of Dental Implant Failure:
Bad Oral Habits – Plaque build-up that leads to infections such as peri-implantitis.
Surgical mistakes:- Incorrect placement of the prostheses can fail.
Bone Resorption – Too little bone to support the implant can lead to implant failure.
Illnesses – Diabetes and osteoporosis have an impact on the healing.
Smoking – It slows down healing and blood flow to the skin.
Can a dentist mess up implants?

Yes, mistakes can be made by a dentist, and the implants can fail as a result. Improper placement, subpar surgical skills, or use of low-quality implants can lead to problems such as infection, nerve injury, or loosening of the implant.
How a Dentist Can Cause an Implant to Fail:
Bad Positioning – Implants that aren’t properly aligned can result in a poor bite.
Nerve Injury – If the implant is incorrectly placed near a nerve, you can experience pain and loss of feeling.
Poor bone evaluation – Failing to take X-rays to ensure there is enough bone before insertion.
Dirty Environment – promotes the possibility of acquiring any infection.
Cheap Materials – May cause the implant to tear or break.
Who should not have dental implants?

Those with uncontrolled diabetes, severe gum disease, a heavy smoking habit, or a lack of adequate bone are not ideal candidates for dental implants. You need them to do a complete evaluation.
Who Shouldn’t Get Dental Implants?
Uncontrolled Diabetes – The healing process is slowed, and the likelihood of infection is high.
Advanced Periodontitis – May lead to instability of the implant.
Heavy Smokers – The risk of implant failure increases because of weakened healing ability.
Not Enough Bone – A Possible bone graft is needed.
Autoimmune Conditions – May delay healing and increase the risk of rejection.
What does dental implant failure look like?

Then, failure of a dental implant may manifest as pain, swelling, the implant moving, or recession of the gums. Give a feel of the implant; if it’s loose or there is continued pain, it may have failed.
Symptoms of Dental Implant Failure:
Offensive and Continued Pain-Swelling-Infection can be offset by maintaining oral cleanliness.
Loosening of the Implant – It should not shift post-fixation.
Receding Gums – May reveal the implant.
Discharge of pus or blood – Indicating an infection.
Chewing Problems – When the implant does not feel tight.
How do you know if you have nerve damage from dental implants?

Nerve injury due to dental implants might lead to numbness, tingling, burning sensations, or even paresthesia of the lips, chin, and tongue. With persistence of symptoms, an urgent assessment was warranted.
Signs of Nerve Damage After Tooth Implant:
Paresthesias – Lips, chin, or tongue may feel numb or tingly.
Burning or Stabbing Pain is not normal pain to have around the implant.
Speaking/Eating Trouble– Loss of muscle control – Any loss of muscle control.
Pain that Won’t Go Away – Pain that persists.
Loss of Taste – If your taste nerves are damaged.
How do you know if something is wrong with your implants?

If your dental implant feels loose, hurts, or causes swelling and recession of the gums, something could be up. Other causes may be infection, implant failure, or bone loss, all of which should prompt a dentist review.
Indications for an Issue with Dental Implants:
Chronic Pain – A continuous dull ache or shooting pain is not normal.
Inflammation or swelling – May be a sign of infection or inflamed gums.
Implant -Lax – MUST NOT MOVE AFTER HEALING.
Receding Gum – If the implant base is visible, this is a poor indication.
Problems with eating – If the implant is loose.
What are the symptoms of dental implant toxicity?

Toxicity symptoms from dental implants can manifest as fatigue, headaches, dizziness, joint pain, or an allergic response. That is triggered by a negative reaction of the body to the titanium or to another material used for the implant.
Typical Signs of Implant Illness:
METAL ALLERGIES- Itching rashes, Swelling, Redness.
Fatigue – All-over tiredness or weakness.
Neurological – Brain fog, dizziness, memory issues.
Joint or Muscle Pain – Body aches for no reason.
Whole-Body Inflammation – Swelling or pain, or even attack-type symptoms as seen in autoimmune diseases.
How do I know if my implants need to be removed?

When to remove a dental implant. Dental implants may be removed if they are loose, painful, or infected, and these symptoms do not improve after a short period. X-rays and an examination of symptoms can determine whether an implant needs to be replaced.
Signs You Might Need to Remove the Implant:
Extreme Pain – Chronic pain suggests likely failure.
Persistent Infection – Chronic infections may necessitate excision.
Bone Loss – When X-rays reveal that the bone is receding.The The
Implant Is Too Loose – Implant shifting its place is a sign of failure.
Gum Recession – If exposed threads are exposed, it may need to be treated.
Can your body reject titanium screws?

Yes, it is rare, but some people have an allergic or immune reaction to the titanium, and their body will swell, and it will be painful, and the implant will fail.
Causes Of Titanium Screw Being Refused:
Allergic Reaction to Metals – Increased sensitivity can lead to an inflamed area.
Autoimmune Response – Your body sees titanium as a foreign object.
Bad Bone Integration – For a successful implant, bone needs to integrate around it; a lack of this integration is a cause of failure.
Persistent inflammation – Redness and discomfort around the breast implant.
Infection – Can prevent the bone and the implant from fusing in the right way.
What are the side effects of titanium screws in the body?
In general, titanium screws are safe, although there are some reports of people experiencing allergic reactions, metal toxicity, and long-term inflammation.
Potential Risks of Titanium Bolts:
Swelling and Pain over the implant site.
Skin Problems – Itching, redness, or rash on the skin.
Toxic Metal – Sometimes very discreet problems (body fatigue) or rare systemic problems.
Loss of bone- It may occur if the body does not heal around the implant.
Nerve Impingement – Can trigger tingling or numbness in certain individuals.
What percentage of people reject dental implants?

The failure rate of implants is around 5-10%, so most have been able to integrate implants. It is uncommon for it to be rejected, but it can occur if the jaw becomes infected, the bone is of poor quality, or the bone fails to heal completely.
Risk Factors for Implant Loss:
Tobacco Use – Limits the blood supply and hinders the healing process.
Diabetes – Shown to impact bone integration and healing.
Bad hygiene of the mouth – Infection with gum disease.
Things to consider: Bruxism (Teeth Grinding) – Might exude enough force to harm implants.
Poor Bone Quality – Low-quality bone may not handle the implant.
What makes you a bad candidate for dental implants?

You might not be suitable for dental implants if you have low bone density, certain medical issues that are out of your control, or poor oral hygiene. A dentist will assess this risk when uncovering the wisdom teeth and advising on treatment.
Why Might Someone Not Be Eligible for Implants?
Significant Bone Loss – The Jawbone is not sufficient to host an implant.
Poorly Controlled Diabetes – Interferes with healing, increases the risk of infection.
Smoking reduces blood and healing capabilities.
Active Disease, Gums, and Infections undermine the supporting structures.
Bruxism (Grinding) – Overforce can cause damage to the implants.
Immune System Deficiency – When your immune system is compromised (due to autoimmune diseases, for example), healing can be compromised as well.
Does insurance cover dental implants?

Most dental benefit plans don’t cover implants completely, but some pay for portions, such as the crown or extractions. It varies by policy and medical necessity.
Possible Insurance Coverage
Simple Dental Plans – Commonly have no benefit for implants, but only for dentures.
Premium Plans – Perhaps a percentage of the cost of implants will be covered.
Dental Insurance – Does not cover implants; (can offer a discount plan to participate in the following carrier) / Note: The only medical insurance that covers implants is if a tooth was lost in an accident.
Believe it or not, a few companies pay for implants.
Payment Plans- Some clinics offer you the chance to finance.
What is the cheapest way to fix messed-up teeth?

The least expensive course of action will be determined by the state of your teeth. From simple fillings to dentures and even dental bonding, there are solutions.
Budget Fixes for Bad Teeth:
Fillings – Most affordable option for shallow cavities.
Dental Bonding – An Inexpensive solution for chips and gaps.
Dentures – Less expensive and more affordable than implants.
Dental Discount Plans – Offer a discounted price for treatment.
Tooth Removals – If you can’t afford to save the tooth.
Can horrible teeth be fixed?

Yes, even teeth that are in very bad shape can be corrected with treatments such as crowns, veneers, implants, or total mouth transformation. The best solution is to get a recommendation from a dentist, who will let you know the best route to take depending on how bad the damage has been.
Ways to Restore Bad Teeth:
Crowns – Restore weakened or fractured teeth.
Veneers – Disguise stained or damaged teeth.
Implants – The ideal replacement for missing teeth.
Braces – Get aligned teeth. Aligners – Get the smile you always wanted.
Full Mouth Restoration – A combination of several treatments.
Where to go if your teeth are really bad?

If your teeth are not in good shape, see a dentist, dental clinic, or specialist for examination. Other cheap alternatives are community health centers, dental schools, and government programs.
Where to Find Help for Bad Teeth:
General Dentist – Primary contact for diagnosis and initial treatment.
Prosthodontist – Expert in replacing damaged teeth.
Oral Surgeon (for extractions or implants).
Community Clinics: These clinics provide low-cost or free dental care.
Colleges of dentistry – Offer services at reduced rates.
What to do if all your teeth are rotten?

If you have tooth decay in all of your teeth, you might have to undergo full extractions and replacements, such as dentures or implants. Don’t delay, get to a dentist before the infection gets out of hand.
Treatment Options:
Complete (Full) Dentures – An affordable treatment option to recreate an entire set of teeth.
Dentures Anchored in Implants – Dentures that are more secure than traditional dentures.
Dental Bridges – Permanent solution for lost teeth.
Full Mouth Reconstruction – A series of procedures in one.
Antibiotics Pain Management – If there is an Infection.
How to fix missing teeth without implants?

If you prefer, implants are not an option; you can use options like dentures, bridges, and partial prosthetics. These treatments return normal function and appearance.
Replacement of Missing Teeth: Not Involved with Implants:
Out-of-Date Dentures – Economical and removable alternative.
Dental Bridges – A fixed option that links to neighboring teeth.
Resin-bonded bridge – Ideal for front teeth replacement.
Snap-On Smile: Similar to an alternative for missing teeth.
Flippers – Transient teeth replacements that can be taken out.
Can terrible teeth be saved?

Yes, many teeth that are deeply damaged can be salvaged with crowns, root canals, or deep cleaning. If they are too decayed, they may have to be removed.
Ways to Save Bad Teeth:
Root Canal Treatment – Kills infection in the roots.
Dental Crowns – Restores and fortifies fragile teeth.
Scaling & Deep Clean – Get rid of the gum bacteria.
Gum Grafting – Correction of gum recession over teeth.
Bone Grafting – Replaces loss of bone to provide support.
Are there any alternatives to dental implants?

Yes – the alternatives are dentures or removable prosthetic bridges. The ideal one depends on your dental health and the size of your budget.
Alternatives to Implants:
Dentures – A cost-effective, removable option.
Fixed Dental Bridges – Supported by surrounding teeth.
Bombs – Temporary, heavy equipment replacements. Flippers – Short-term, expendable flippers.
Snap-On Smile – Not permanent, but an aesthetic choice.
Resin-Bonded Bridge – Appropriate for the replacement of front teeth.
Can I get a refund for a failed dental implant?

Whether a refund on a bad dental implant can be given or not depends on the policy of the dentist and the reason for failure. A few clinics refund a portion or the full amount, and others offer corrective treatment in place of the refund. This is probably worth discussing before treatment happens.
Refund Eligibility Determining Factors:
Dentist’s Policy: Some may have guarantees, others may not.
Reasons for Failure: In the event of failure through incorrect positioning, it may be refunded or rectified.
The Patient’s Responsibility: The Guarantee is void if oral hygiene is neglected or you smoke.
Other Options: Insurance may cover revisions.
Legal: When malpractice is the issue, all legal options are possible.
Make sure to talk about refund policies and warranties with your dentist before agreeing to get an implant in order to save some money.
Does insurance cover dental implants?

Most insurance plans do not pay for implants; they may or may not foot part of the bill for the procedure, such as extractions, sedation, or crowns. Partial coverage may be available with certain premium plans or supplemental insurance. For specific benefits, refer to the details of your policy.
Ways Insurance Can Help:
Limited Coverage: Some plans cover exams, X-rays, and extractions.
Partial Coverage: Some plans will cover a portion of the implants.
Supplemental Plans: You may want to purchase an extra policy or a dental discount plan.
Health Insurance: Coverage could be provided if implants are medically required.
Employer Coverage: Some companies have insurance policies that include implants.
Always check with your insurer to find out what your options are.
How to pay for dental implants with bad credit?

Some options can help if you have bad credit, including dental financing plans, credit-building loans , and alternative payment methods. Most dentists also provide easy payment options that could make implants less pricey.
Financing Options:
In-house Financing: Monthly payments are an option at many clinics.
Medical Credit Cards: Anyone in need of financing dental work can use programs like CareCredit.
Personal Loans: Some lenders will loan money to those with bad credit.
Government Aid: Some costs may be covered by Medicaid and other programs.
Dental Schools- reduced cost services rendered at teaching facilities.
Review and compare which offers the best options for the solution for your budget.
How to get dental implants with bad credit?
Having no credit does not preclude you from dental implants, and it is possible through other means of payment, such as alternative financing, low-cost clinics , or insurance help. Many providers have flexible payment options for patients with bad credit.
How to Get Implants with Bad Credit:
Look for In-House Financing: There are plenty of dentists who provide payment plans without the need for a credit check.
Leverage Healthcare Credit Cards: Certain lenders will accept loan applicants with lower scores.
Consider Low-Cost Dental Clinics: Local clinics can offer less expensive care.
Seek Government Help: Medicaid or veterans’ benefits might be available.
Think About Dental Tourism: In some countries, you can get implants for much less money.
If possible, look at all options to get the most affordable implant that’s right for you.
Are dental implants bad for your health?

Implants are typically safe and effective if you have the procedure performed by a trained expert, but if you don’t take care of them properly, you can still experience complications. Complications, including infection, bone loss, and implant failure, and especially common in people who have certain medical conditions and who smoke, have poor oral hygiene, or are not well enough to practice rigorous oral hygiene.
Possible complications of dental implants:
Infection – Lack of good oral hygiene can result in peri-implantitis, an inflammatory process that leads to bone loss and can cause the implant to fail.
Nerve Damage – In some cases, if not properly placed, the implants can push on nerves and bring about pain or numbness.
Sinus issues – An implant in the upper jaw may extend into one of your sinus cavities, resulting in sinusitis.
Bone Resorption – Implants may be lost without integration and result in bone loss.
Medical Problems – Diabetics, people with osteoporosis, and those who have immune disorders are more likely to develop complications.
Effects of Smoking – Tobacco use can slow the healing process and lower the likelihood of implant success because it decreases the blood supply.
If you maintain good oral hygiene, receive routine dental checks, and listen to your dentist, implants are a safe and long-term solution to lost teeth.
Why are dental implants bad?

Dental implants are not evil, but that does not mean they are right for all. Bad oral hygiene, tobacco use, or underlying health conditions can raise the likelihood of an implant failing, gum disease, or loss of bone, all of which can cause complications.
What Are the Causes of Some People Thinking Dental Implants As a Risk?
Pricey – Implants can be quite expensive and are not usually covered by insurance.
Possible Surgical Complications – Infection, swelling, and nerve damage.
Lengthy Recovery Time -May require months of rest and recovery.
Bone Grafting – In some cases, patients require additional surgery to bolster their weakened jawbone.
Rejection of Implant – It occurs very seldom, but the body can reject the implant.
And is safe and long-lasting for most people, however, a dentist should be consulted to determine if implants are right for you.
Why are dental implants a bad idea?

Most people are not bad candidates for dental implants, but they’re not right for all, especially those with low bone density, poor health, or money issues. Complications such as infection, bone loss , and protracted healing periods are possible.
When Are Dental Implants Not the Right Option?
Health – Diabetes, osteoporosis, and immune disorders all increase the possibility of failure.
Smoking – This raises both the chances of infection and the healing time.
Underdeveloped Jawbone – Needs more grafting surgery.
Expensive – You’re talking thousands, typically not covered by insurance.
Time-consuming –The Entire process spans over a few months.
Implants are a permanent treatment for a missing tooth, provided the patient practices good oral hygiene and follows the post-surgical after-care.
Why is smoking bad for dental implants?

Smoking is harmful to dental implants as it limits blood circulation, slows down the healing process, and increases the risk of infection. Smokers have a far greater incidence of implant failure than non-smokers.
Consequences of Smoking on Dental Implants:
Delayed Healing –Less blood flow due to nicotine slows down the process of the bone integrating.
Higher risk of infection – The immune response is weakened when exposed to smoke, which gives way to infections.
Lower Success Rate – Smokers’ studies show the success rate is 2-3 times lower.
Gum Disease— Smoking raises your risk of peri-implantitis, which can result in implant failure.
Bone Density – Smoking in the long run can make tooth loss and implants unstable, due to bone loss.
Smoking cessation before and after the surgery has been found to notably increase the success of the implant.
Do dental implants cause bad breath?

Yes, dental implants can lead to bad breath when not well managed, and infection is present. Bad breath can be a result of poor oral hygiene, food impact, or peri-implantitis (gum infection around the implant).
What Are The Reasons For Bad Breath From Implants?
Bad Oral Hygiene – Plaque can form on the implant, and this can be a site for bacteria growth – as a rule of thumb, it is always easier to eliminate odor caused by plaque than general “bacteria.
Food Debris – Debris stuck under or near the implant can rot and smell bad.
Infection Around the Gums (Peri-implantitis) – An infection around the implant that can generate pus and smell.
Dry mouth – This means not having enough saliva, which can allow bacteria in the mouth to grow and cause bad breath.
Tobacco – Tobacco compromises healing and can cause bad breath to linger.
How to Prevent It:
Brush and clean around implants every day.
Use antibacterial mouthwash.
Have regular dental checkups to catch infections early.
Keep yourself hydrated and stop smoking.
Also Read>>>Endosteal Implants: A Complete Guide to Costs, Benefits & Procedure!
Also Read>>>Full Mouth Dental Implants Cost in 2025: Breakdown, Factors & Ways to Save

Dr. Niraj Ghanghoriya is a passionate dental surgeon with over 12 years of experience in clinical dentistry. He completed his BDS from the prestigious Sri Aurobindo Institute of Dentistry in 2012 and specializes in painless root canals, smile makeovers, and preventive oral care. He is the Founder of ToothCareUSA.com and a registered Dental Surgeon (Reg No: A-03649) based in Indore. Known for his patient-first approach and clear communication, Dr. Ghanghoriya aims to make dental knowledge accessible to everyone. When he’s not in the clinic, he enjoys writing informative dental blogs to help people take better care of their oral health. He reviews every article on this site to ensure medical accuracy and patient safety.